CIHR Health Research and Health-Related Data Framework and Action Plan
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Vision
- Definitions
- Guiding Principles
- Desired Outcomes & Objectives
- Action Plan
- Conclusion
- Appendix 1: CIHR Health Research and Health-Related Data Framework and Action Plan Visual
Introduction
The global data revolution is having a profound impact on health research. As the volume, flow and complexity of health research and health-related data increases, new challenges and opportunities are emerging that range across a spectrum of disciplines and jurisdictions. Governments, researchers, research institutions, publishers and other stakeholders are increasingly recognizing data as a valued output of research, as evidenced by the international movement towards open research and open data. Additionally, health research and health-related data are increasingly understood to be an important input into new research and the evidence base. For example, pre-existing datasets from research and non-research sources are being re-used to answer real-world complex questions. The data revolution is also being driven by the rapid production of new and novel data sources resulting from growth in electronic health systems, technologies and digital culture. Like other countries, Canada seeks to leverage the evolving digital data landscape in order to support excellence in health research and knowledge translation.
As Canada's federal funding agency for health research, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) plays an active leadership role in the data ecosystem. CIHR's strategic plan, Health Research Roadmap II, includes a commitment to embrace the data revolution by advancing data-intensive research, and seizing upon the transformative power of information and communication technologies. CIHR recognizes that we are just one player in a rapidly changing space, and that our ability to deliver on this commitment depends on strong relationships with other stakeholders in the data ecosystem. Working closely with partners, CIHR promotes and enables data-intensive research and data stewardship through a multi-pronged approach which includes the design and delivery of strategies, policies, platforms, initiatives, funding opportunities and events.
Given CIHR's active involvement in a multitude of data-related endeavours, a framework has been developed to ensure a cohesive and consistent approach. The CIHR Health Research and Health-Related Data Framework and Action Plan (the Framework) provides a shared vision, guiding principles, desired outcomes, objectives and actions to guide current and future data-related activities so as to maximize impact.
Vision
To advance knowledge, expand research opportunities, and improve health services, products and outcomes by effectively accessing, analyzing, linking, integrating, using, reusing, storing and preserving health research data and health-related data in Canada.
Definitions
Given the many sources and forms of data, definitions are provided below for the different types of data referred to within this Framework. While CIHR recognizes that some datasets may conceptually fit into more than one data type, the following categorizations provide a simplified way to discuss these data at the high level appropriate within the Framework.
- Health Research Data: Data generated through scientific inquiry across the health research spectrum and required to validate findings. This includes both human (e.g. randomized control trials) and non-human data.
- Health System Data: Data on official health status of individuals (e.g. well-being, health conditions), health system performance (e.g. accessibility, effectiveness), and health system characteristics. Examples include administrative, clinical and population health data.
- Population Health Data: A type of health system data that includes data on the social, cultural and environmental factors that affect the health of populations, as collected through health surveys, public health surveillance systems and longitudinal studies.Footnote 1
- Health-Related Data: Data on non-medical determinants of health such as behaviours, living and working conditions, personal resources and environmental factors.
- Consumer Data: A type of health-related data that includes data collected about consumers through social media, online browsing, mobile applications and purchasing history.
- Social Science Data: A type of health-related data that includes data on human society and social relationships such as health behaviours, living and working conditions, personal resources and environmental factors.
Guiding Principles
Underpinning this Framework are six guiding principles that CIHR will integrate into its data-related activities. The health research community is also strongly encouraged to adhere to these principles when pursuing data-intensive research and engaging in data stewardship.
- Integrity: Ensure and maximize data quality, as a foundational element.
- Stewardship: Optimize benefits of open access to data while ensuring privacy and respecting rights, ethics and cultural meaningfulness.
- Value: Acknowledge the contributions of researchers and data professionals, and respect the intellectual property rights of data owners.
- Discoverability: Ensure data is visible and usable by others.
- Sustainability: Plan for long-term preservation, curation, and use of data.
- Proactivity: Anticipate and plan for future data needs and opportunities.
Desired Outcomes & Objectives
Based on CIHR's mandate and position within the research data ecosystem, four data-related outcomes have been selected.
The desired outcomes and associated objectives are as follows:
- A collective digital culture is fostered: Foster, encourage, recognize, and promote leadership and excellence in data management, data sharing, and the use of novel data sources.
- Required data-related resources are available: Support the development of tools, methodologies, platforms, and new assets to enable data management and data-intensive research.
- Relevant data-related skills are expanded: Develop and expand skills in data science, data management and data stewardship.
- Data access, linkage, use and reuse are enabled across Canada: Promote better data attributes (data quality, access, linkage, integration and utility) as integral to excellence in research and knowledge translation.
Action Plan
To achieve the four desired outcomes, associated objectives and the overall vision, CIHR proposes to undertake the following actions:
- Collective Culture
Fostering a research culture that recognizes data as a valuable resource and enables excellence in data management, including data sharing, will benefit all members of the data ecosystem. Collaboratively developing new norms with other stakeholders in the health research community will encourage leadership and create new opportunities for collective action.
Action 1: CIHR will develop and adopt policies and guidelines to support effective stewardship and sharing of data generated and used for research.
CIHR has already made significant efforts focused on changing culture through policy. For example, CIHR co-led the development of the Tri-Agency Statement on Digital Data Management (2016), which outlines agency expectations related to digital data management and describes the responsibilities of various actors within the data ecosystem. CIHR is also a signatory on two international joint statements led by the Wellcome Trust promoting the need for data sharing in public health. The first statement, Sharing Research Data to Improve Public Health (2011), openly communicates a joint commitment to increase the availability of research data to the scientific community and to promote the efficient use of this data to further advancements in public health. The subsequent Statement on Data Sharing in Public Health Emergencies (2016), calls for all research data collected during public health emergencies to be made publically available as quickly and openly as possible. Additionally, as a member of the Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (GA4GH), CIHR has endorsed the foundational principles and core elements outlined within the GA4GH Framework for the Responsible Sharing of Genomic and Health Data (2014). Moving forward, CIHR will continue to lead and collaborate on the development of policy statements and guidelines to promote research data quality, access and sharing.
Action 2: CIHR will establish mechanisms to incentivize and recognize excellence in data management, data sharing and innovative uses of data.
CIHR is exploring a variety of opportunities to capture and encourage innovative data-intensive research and excellence in data stewardship. For example, CIHR intends to partner on funding opportunities to stimulate the identification and use of non-traditional data sources and methodologies, as well as to link existing cohort datasets with administrative and clinical data.
- Required Resources
Insufficient infrastructure, tools, funding and other resources are recognized as barriers to realizing the full potential of the data revolution. In Canada, a number of organizations, including CIHR, are working together to develop and share potential solutions to address these barriers.
Action 3: CIHR will raise awareness of internal and external data-related resources, including tools, platforms and existing datasets.
CIHR has launched a Health Research Data webpage that highlights relevant CIHR-led and supported Initiatives, strategies and policies. It also features CIHR-funded and external data resources, such as platforms, training programs and publications. Additionally, the webpage lists key stakeholders that CIHR is engaging with to further the Canadian research data landscape.
Action 4: CIHR will collaborate with stakeholders to create new opportunities to advance data stewardship and develop the necessary infrastructure.
CIHR is engaging with a wide variety of stakeholders within the research data ecosystem to address data-related barriers. For example, CIHR is an active member of the Research Data Canada (RDC) Steering committee and Policy Subcommittees, with the goal of helping to enhance access to research data and improve research data management within Canada. CIHR is also an observer on the Leadership Council for Digital Infrastructure (LCDI), a national collaboration of stakeholders committed to advancing Canada's digital infrastructure ecosystem, and the Committee on Data for Science and Technology (CODATA), an interdisciplinary group working to improve the quality, reliability, management and accessibility of numerical data to all fields within the science and technology community.
- Relevant Skills
To contribute to and benefit from the data revolution, Canadian researchers, peer reviewers and other stakeholders must be able to gain access to training and/or individuals with relevant skills, such as capacity to analyze or manage data.
Action 5: CIHR will design and implement strategies to build and integrate data-related capacity.
CIHR continues to design and implement strategies to enable the growth and integration of data-related research capacity. For example, CIHR has developed a Strategic Plan on Training that includes a specific commitment to build capacity in data-intensive research. CIHR is also working with the bioinformatics and computational biology research community to explore how such skills could be better integrated across the life sciences.
Action 6: CIHR will collaborate with stakeholders to build data science capacity within the health research community.
CIHR is an active member of a Federal, Provincial and Territorial (F/P/T) committee focused on health analytics capacity. CIHR is also engaging with other Federal partners, such as Statistics Canada, regarding opportunities to collectively build the cadre of Canadian data scientists.
Action 7: CIHR will support training and partnership opportunities that enhance data-intensive research capacity.
Several of CIHR's large strategic investments include a strong focus on building data-related capacity. For example, the Strategy for Patient Oriented Research (SPOR) Support for People and Patient-Oriented Research and Trials Units (SUPPORT Units) offer training programs on the secondary analysis of existing large datasets for patient-oriented research, data management and biostatistics. Additionally, the Drug Safety and Effectiveness Network (DSEN) is building capacity related to the meta-analysis of big data.
- Enable Access, Linkage, Use and Reuse
The data revolution depends on increasing responsible access, linkage, use and reuse of research data in all areas of research. However, norms related to access and sharing vary across research disciplines, institutions and jurisdictions, and can create uncertainty among data producers and data users. Promoting better data attributes across the health research ecosystem will increase opportunities for excellence in both research and knowledge translation through the better use of available data sources.
Action 8: CIHR will fund initiatives that strengthen data quality, access, linkage, integration and utility.
CIHR continues to make significant investments into Initiatives with objectives and components specifically designed to enable data access, sharing, linkage and reuse. For example, CIHR has provided targeted funding for the creation of data platforms through the SPOR SUPPORT Units ($125M), the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging ($65M) and the Canadian Research Data Centre Network ($16.9M). CIHR has also funded numerous Initiatives with a data-intensive research focus, such as DSEN, the Canadian Consortium on Neurodegeneration in Aging (CCNA), the Canadian Epigenetics, Environment and Health Research Consortium (CEEHRC), and the GA4GH amongst others. In addition, many of CIHR's emerging strategic investments, such as the Healthy Life Trajectories Initiative (HeLTI), include objectives related to the sharing of data both within Canada and internationally. CIHR is also exploring new partnering opportunities to support the linkage and reuse of existing cohort, administrative and clinical datasets.
Action 9: CIHR will collaborate with stakeholders to advance data access, sharing, linkage and integration, including across jurisdictional and sectors.
CIHR is a member of a F/P/T committee focused on overcoming barriers to data sharing across jurisdictions. Additionally, CIHR's investment in SPOR has already resulted in the identification of opportunities for responsible access and linkage of health system data within and across provincial boundaries. CIHR is also exploring options for how to best share data across international boundaries through its involvement with the Global Research Collaboration for Infectious Disease Preparedness (GloPID-R) and its working group on data sharing in public health emergencies. This working group exemplifies how CIHR can continue to constructively work with international partners to further shared data-related priorities and maximize the collective potential of research investments.
Conclusion
CIHR's role in advancing the digital ecosystem for health research will continue to grow and evolve in response to the needs of the research community, the public and our many Canadian and international partners. The Framework provides a vision and guiding principles that support coordination and consistency, and sets outcomes and objectives that demonstrate our commitment to ongoing leadership in the digital ecosystem. CIHR will use this Framework to inform current and future activities as we work with stakeholders to advance excellence in data-intensive research and data stewardship.
Appendix 1: CIHR Health Research and Health-Related Data Framework and Action Plan – A Visual
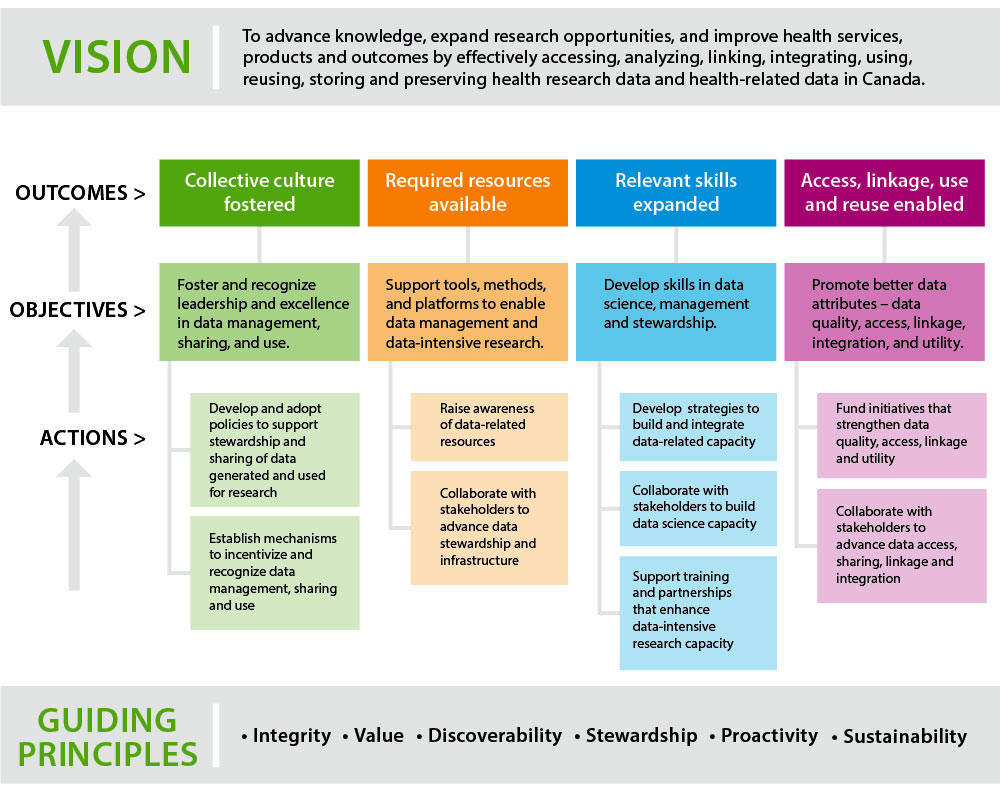
Long description
Health Research and Health-Related Data Framework and Action Plan
Vision:
To advance knowledge, expand research opportunities, and improve health services, products and outcomes by effectively accessing, analyzing, linking, integrating, using, reusing, storing and preserving health research data and health-related data in Canada.
Guiding Principles:
- Integrity
- Value
- Discoverability
- Stewardship
- Proactivity
- Sustainability
Outcomes and Objectives:
A collective culture:
Foster and recognize leadership and excellence in data management, sharing, and use.
- Action 1: Develop and adopt policies to support stewardship and sharing of data generated and used for research.
- Action 2: Establish mechanisms to incentivize and recognize data management, sharing and use.
Required resources available:
Support tools, methods, and platforms to enable data management and data-intensive research.
- Action 3: Raise awareness of data-related resources
- Action 4: Collaborate with stakeholders to advance data stewardship and infrastructure
Relevant skills expanded:
Develop skills in data science, management and stewardship.
- Action 5: Develop strategies to build and integrate data-related capacity
- Action 6: Collaborate with stakeholders to build data science capacity
- Action 7: Support training and partnerships that enhance data-intensive research capacity
Access, linkage, use and reuse enabled:
Promote better data attributes – data quality, access, linkage, integration, and utility.
- Action 8: Fund initiatives that strengthen data quality, access, linkage and utility
- Action 9: Collaborate with stakeholders to advance data access, sharing, linkage and integration.
- Date modified: